Imperial Architecture: Difference between revisions
A. pippenger (talk | contribs) (→Roofs) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
[[File:EA_1B.png| | [[File:EA_1B.png|600px]] | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[[File:EA_3B.png| | [[File:EA_3B.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Pillars2.png| | [[File:EA_Pillars2.png|600px]] | ||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
[[File:EA_2B.png| | [[File:EA_2B.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Arches1.png| | [[File:EA_Arches1.png|600px]] | ||
Variant windows with pillars and arches of differing sizes were used less commonly. Occasionally circular windows were created by putting stair blocks against each corner of a square gap in a wall. | Variant windows with pillars and arches of differing sizes were used less commonly. Occasionally circular windows were created by putting stair blocks against each corner of a square gap in a wall. | ||
[[File:EA_RoundWindows1.png| | [[File:EA_RoundWindows1.png|600px]] | ||
| Line 56: | Line 56: | ||
The most common style of relief was a 3x3 square with a single block jutting out from the center bothom and center top. | The most common style of relief was a 3x3 square with a single block jutting out from the center bothom and center top. | ||
[[File:EA_Reliefs2.png| | [[File:EA_Reliefs2.png|600px]] | ||
Another common style was shaped like a simplified S or Z. | Another common style was shaped like a simplified S or Z. | ||
[[File:EA_Reliefs1.png| | [[File:EA_Reliefs1.png|600px]] | ||
Other styles of relief were sometimes used as well. | Other styles of relief were sometimes used as well. | ||
[[File:EA_Reliefs3.png| | [[File:EA_Reliefs3.png|600px]] | ||
==Exterior Columns== | ==Exterior Columns== | ||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
These columns usually met in an arch shape at the tops, like the common arch windows. Buildings could be covered in multiple layers of exterior columns. | These columns usually met in an arch shape at the tops, like the common arch windows. Buildings could be covered in multiple layers of exterior columns. | ||
[[File:EA_Columns1.png| | [[File:EA_Columns1.png|600px]] | ||
At Ascaris particularly, a style of column was used that leaned outward from the building. These columns had an upside down stair placed against the top block, and usually more stone brick walls were laid on top of these stairs. This allowed houses to get wider as they increased in height. Cinnabars was the inventor and chief expert of this style. | At Ascaris particularly, a style of column was used that leaned outward from the building. These columns had an upside down stair placed against the top block, and usually more stone brick walls were laid on top of these stairs. This allowed houses to get wider as they increased in height. Cinnabars was the inventor and chief expert of this style. | ||
[[File:EA_Columns2.png| | [[File:EA_Columns2.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Columns4.png| | [[File:EA_Columns4.png|600px]] | ||
Sometimes flower bushes and grass were also placed on top of these stairs. | Sometimes flower bushes and grass were also placed on top of these stairs. | ||
[[File:EA_Columns3.png| | [[File:EA_Columns3.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Columns5.png| | [[File:EA_Columns5.png|600px]] | ||
==Roofs== | ==Roofs== | ||
| Line 88: | Line 88: | ||
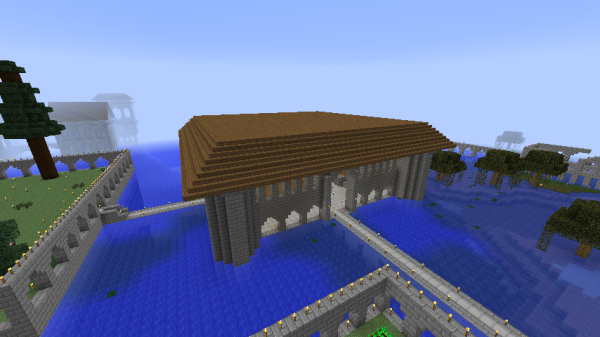
Classic Imperial roofs were almost universally made of spruce planks, stairs, and slabs. In Classic Imperial style, these roofs matched the shape of the building they covered, and formed a simple pyramid shape as the walls met at a peak. | Classic Imperial roofs were almost universally made of spruce planks, stairs, and slabs. In Classic Imperial style, these roofs matched the shape of the building they covered, and formed a simple pyramid shape as the walls met at a peak. | ||
[[File:EA_Roof1.png| | [[File:EA_Roof1.png|600px]] | ||
Some Imperial roofs were similar, but rather than a peak on top, they had a large flat area, in a truncated pyramid or "3d trapezoid" shape. | Some Imperial roofs were similar, but rather than a peak on top, they had a large flat area, in a truncated pyramid or "3d trapezoid" shape. | ||
[[File:EA_Roof2.png| | [[File:EA_Roof2.png|600px]] | ||
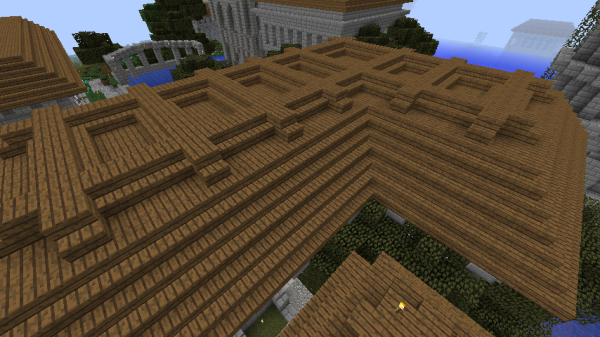
Many roofs followed this basic pattern but had additional detail, particularly Cinnabarian roofs in Ascaris. | Many roofs followed this basic pattern but had additional detail, particularly Cinnabarian roofs in Ascaris. | ||
[[File:EA_Roof3.png| | [[File:EA_Roof3.png|600px]] | ||
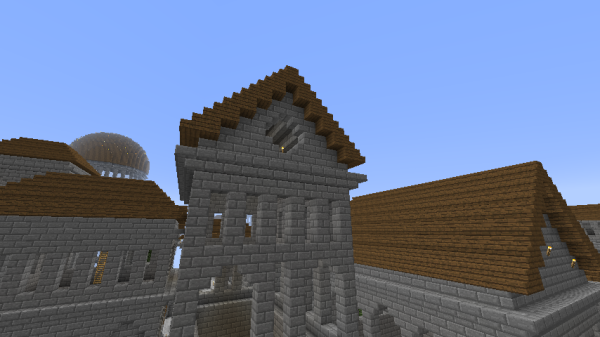
The highest quality Imperial and Post-Imperial roofs, though, were usually in a triangular prism shape, like a typical "log cabin" roof. | The highest quality Imperial and Post-Imperial roofs, though, were usually in a triangular prism shape, like a typical "log cabin" roof. | ||
[[File:EA_Roof4.png| | [[File:EA_Roof4.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Roof5.png| | [[File:EA_Roof5.png|600px]] | ||
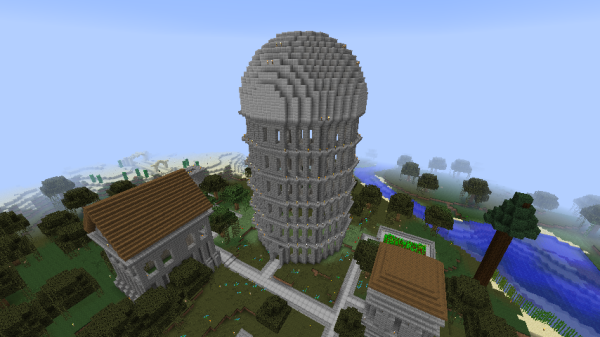
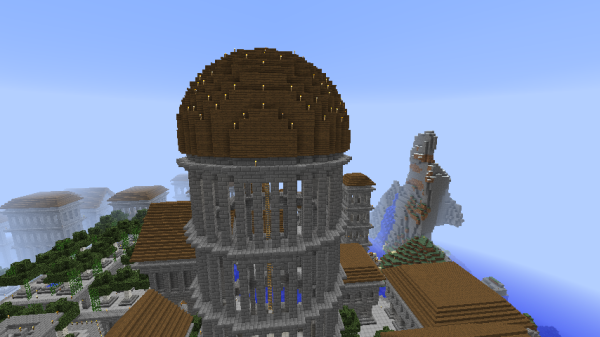
Large circular buildings usually had a sphere-based dome roof made of smooth stone slabs. These were built according to the plotz voxel sphere generator. Spruce domes were also used. Domes are an integral part of both Classic and Post-Imperial Architecture. | Large circular buildings usually had a sphere-based dome roof made of smooth stone slabs. These were built according to the plotz voxel sphere generator. Spruce domes were also used. Domes are an integral part of both Classic and Post-Imperial Architecture. | ||
[[File:EA_Dome2.png| | [[File:EA_Dome2.png|600px]] | ||
[[File:EA_Dome1.png| | [[File:EA_Dome1.png|600px]] | ||
Whatever the style of roof used, almost all examples of Imperial Architecture include a lip of upside down stone brick stairs on the building exterior directly beneath the roof. | Whatever the style of roof used, almost all examples of Imperial Architecture include a lip of upside down stone brick stairs on the building exterior directly beneath the roof. | ||
Revision as of 10:53, 19 July 2015
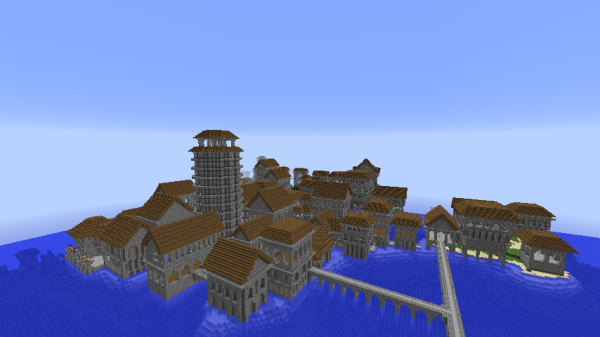
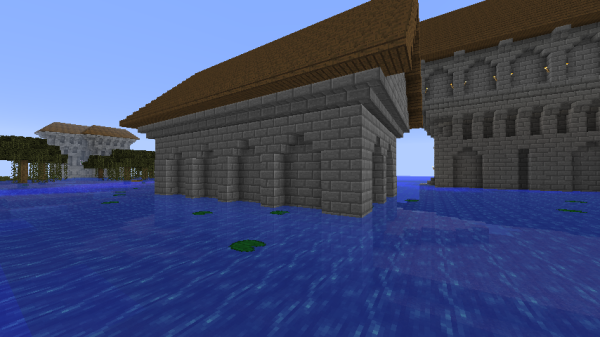
Imperial Architecture is a distinct and unique method of building design utilized by The Empire. The style continued to be learned, used, and improved upon for years after the fall of The Empire in Stonetown, Ascaris, Aggersel, Virunum, and new towns created by The Order.
Classic Imperial Architecture was created by Pippenger in 2013 to be used in New Caladan and other imperial cities. It was a relatively simple style meant to have an elegant and civilized, though easily mass produced, appearance.
Post-Imperial Architecture describes variants used by Pippenger after the fall of The Empire, as well as all improvements made by players who modified the style for themselves. In some cases the Post-Imperial style was considerably more complex than, and superior to, Classic Imperial Architecture. Post-Imperial Architecture reached its peak in Ascaris, where Cinnabars greatly improved the style.
Materials
Rules regarding building materials in The Empire were strict and specific. Stonebrick was the primary material of almost all buildings, with smooth stone slabs and spruce being used for roofs and floors. Cobblestone and most other materials were usually prohibited, and even the use of glass was discouraged.
While these rules were most strict in Classic Imperial Architecture, Post-Imperial Architecture has generally held to them as well.
Windows
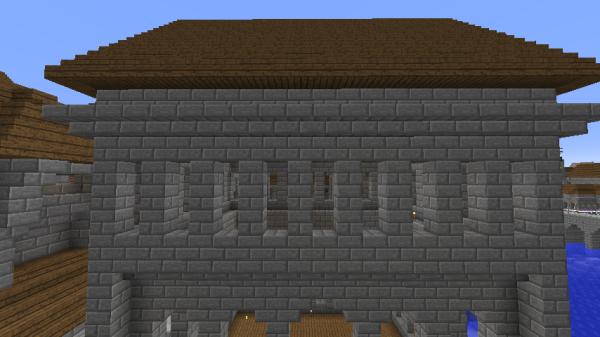
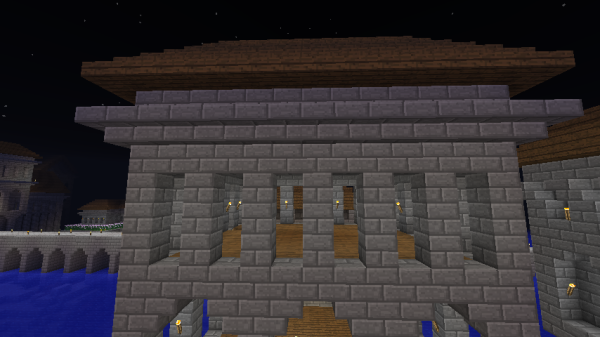
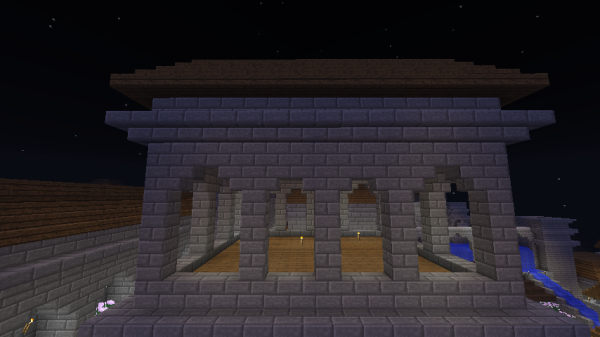
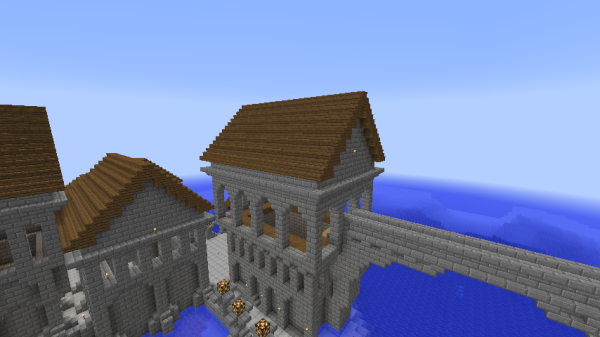
Most imperial buildings had open-air windows, usually built in specific ways. Most common were 1x3 pillar windows in a Romanesque style.
These pillars could be slightly taller or shorter, and occasionally wider.
Taller arched windows were often used as well. These were wider than the pillar windows, usually 2-3 meters, and 4-7 meters in height. At the upper corners were upside down stone brick stairs, giving the windows a natural arch shape.
Variant windows with pillars and arches of differing sizes were used less commonly. Occasionally circular windows were created by putting stair blocks against each corner of a square gap in a wall.
Sometimes, particularly in buildings where defense was an important consideration, slit windows were created with stone brick slabs.
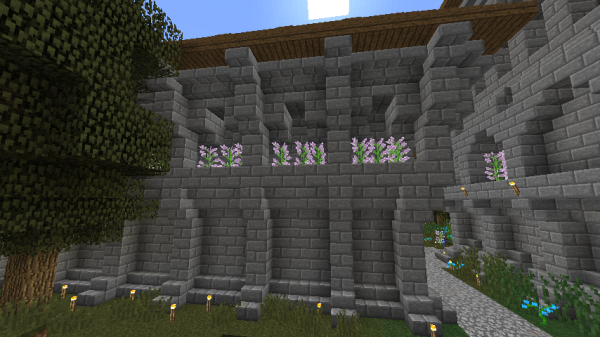
Reliefs
One of the most distinctive features of Classic Imperial Architecture is the method of adding stone brick relief decorations to walls.
These reliefs were most often sandwiched between a row of upside down stair blocks beneath them, and typical stair blocks above them. In this way, imperial buildings were often divided into vertical segments, each segment decorated with different styles of relief or window.
The most common style of relief was a 3x3 square with a single block jutting out from the center bothom and center top.
Another common style was shaped like a simplified S or Z.
Other styles of relief were sometimes used as well.
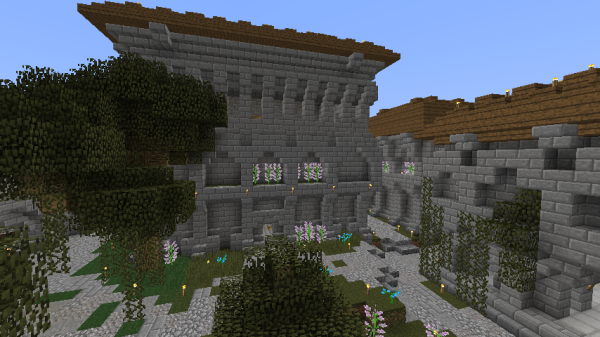
Exterior Columns
Not especially common in The Empire, but very common in Post-Imperial Architecture at the later bases Ascaris and Aggersel, were buildings with columns/pillars laid directly against the exterior walls.
These columns usually met in an arch shape at the tops, like the common arch windows. Buildings could be covered in multiple layers of exterior columns.
At Ascaris particularly, a style of column was used that leaned outward from the building. These columns had an upside down stair placed against the top block, and usually more stone brick walls were laid on top of these stairs. This allowed houses to get wider as they increased in height. Cinnabars was the inventor and chief expert of this style.
Sometimes flower bushes and grass were also placed on top of these stairs.
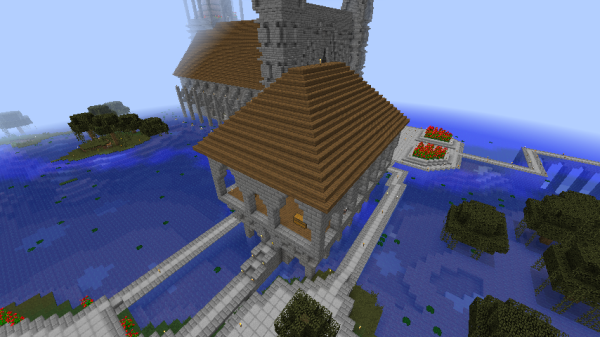
Roofs
Classic Imperial roofs were almost universally made of spruce planks, stairs, and slabs. In Classic Imperial style, these roofs matched the shape of the building they covered, and formed a simple pyramid shape as the walls met at a peak.
Some Imperial roofs were similar, but rather than a peak on top, they had a large flat area, in a truncated pyramid or "3d trapezoid" shape.
Many roofs followed this basic pattern but had additional detail, particularly Cinnabarian roofs in Ascaris.
The highest quality Imperial and Post-Imperial roofs, though, were usually in a triangular prism shape, like a typical "log cabin" roof.
Large circular buildings usually had a sphere-based dome roof made of smooth stone slabs. These were built according to the plotz voxel sphere generator. Spruce domes were also used. Domes are an integral part of both Classic and Post-Imperial Architecture.
Whatever the style of roof used, almost all examples of Imperial Architecture include a lip of upside down stone brick stairs on the building exterior directly beneath the roof.